Best Info About How To Diagnose Pcos
/taking-the-pill-for-pcos-2616584-5c04a331c9e77c000147c55e.png)
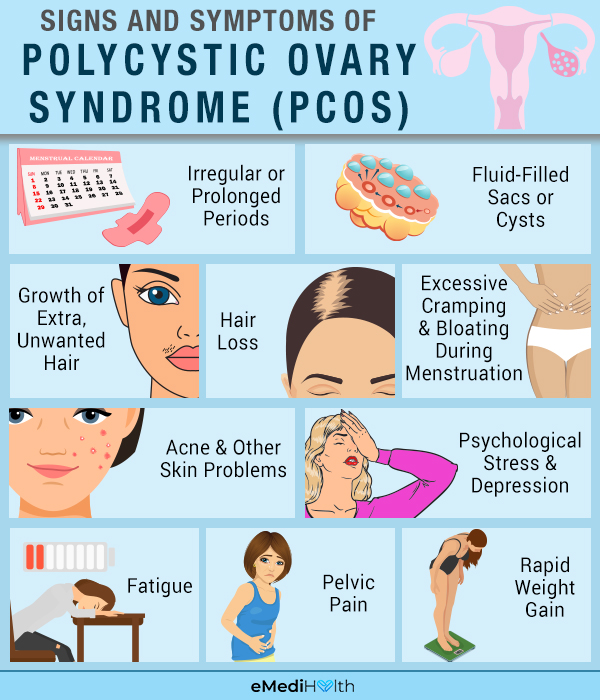
Irregular or absent menses, heavier than normal bleeding,.
How to diagnose pcos. There is no single blood test that can diagnose the disease. Blood tests are one of the first and most important examinations done to determine if a woman is suffering from pcos. Research from 2016 suggests your doctor will ask about your medical history and menstrual cycle to diagnose pcos.
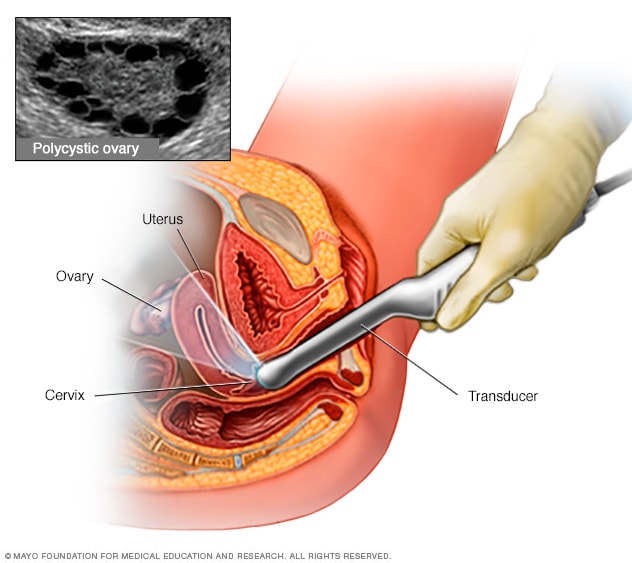
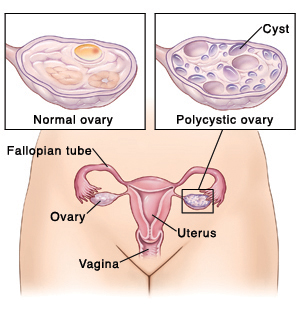
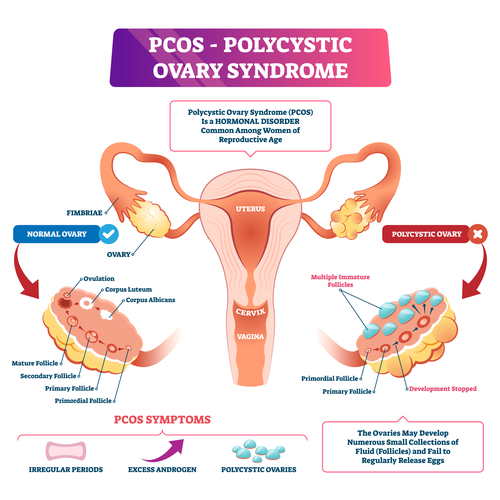
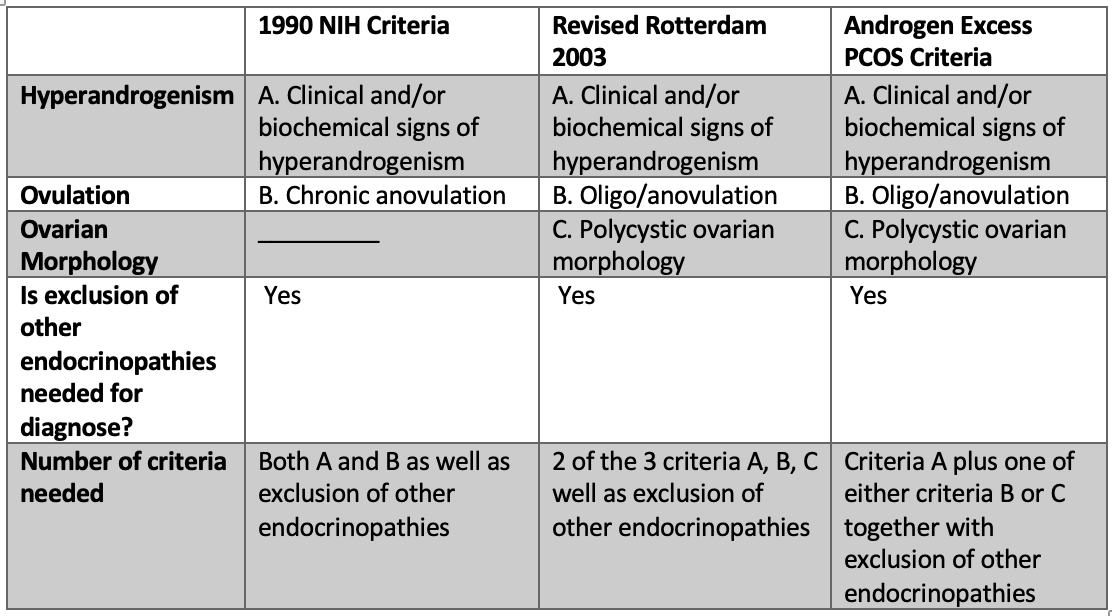
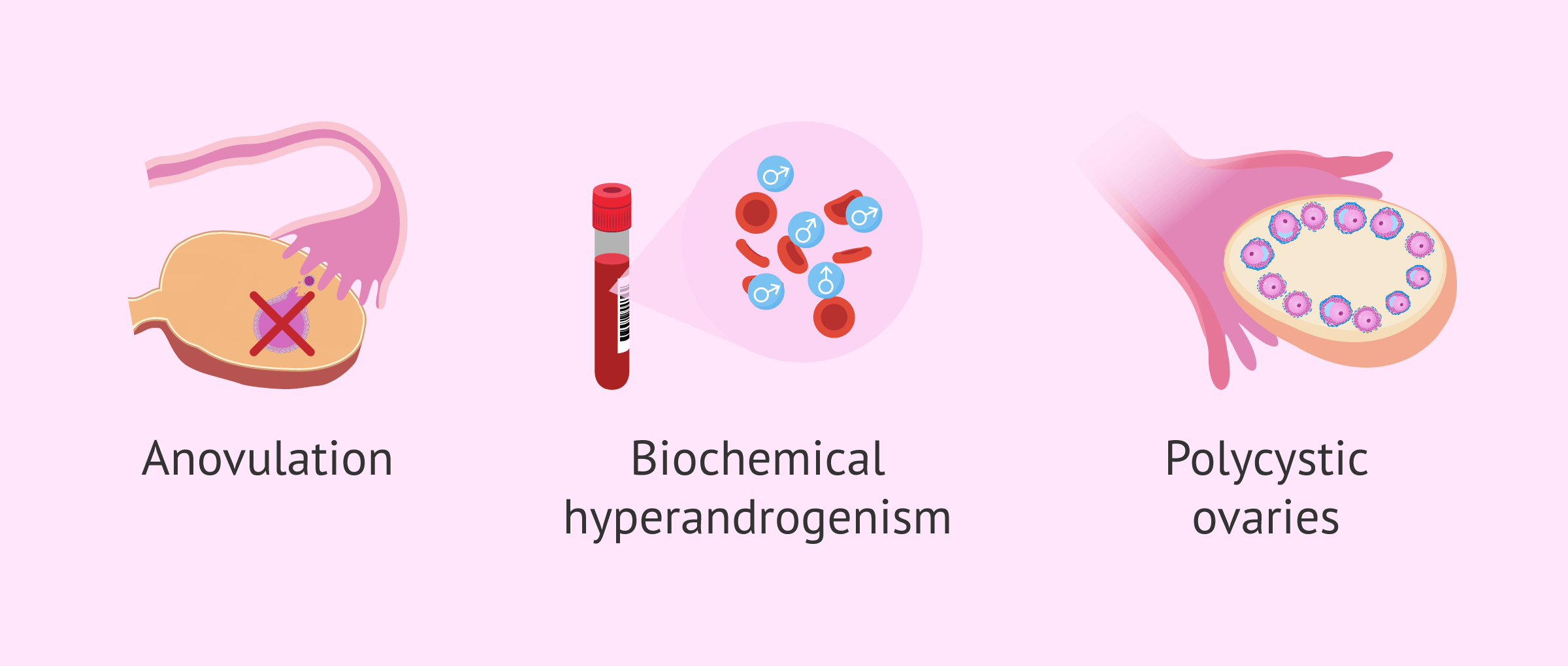
Your doctor may diagnose pcos if you have at least two of these symptoms: A diagnosis of pcos can be made when at least two of the following three criteria are met: Multiple cysts of a specific size on one or both of the ovaries as detected by ultrasound.
They’ll also use ultrasound imaging to look at the number. As such, either serological (blood) or. Your health care provider will use one of three different methods to diagnose.
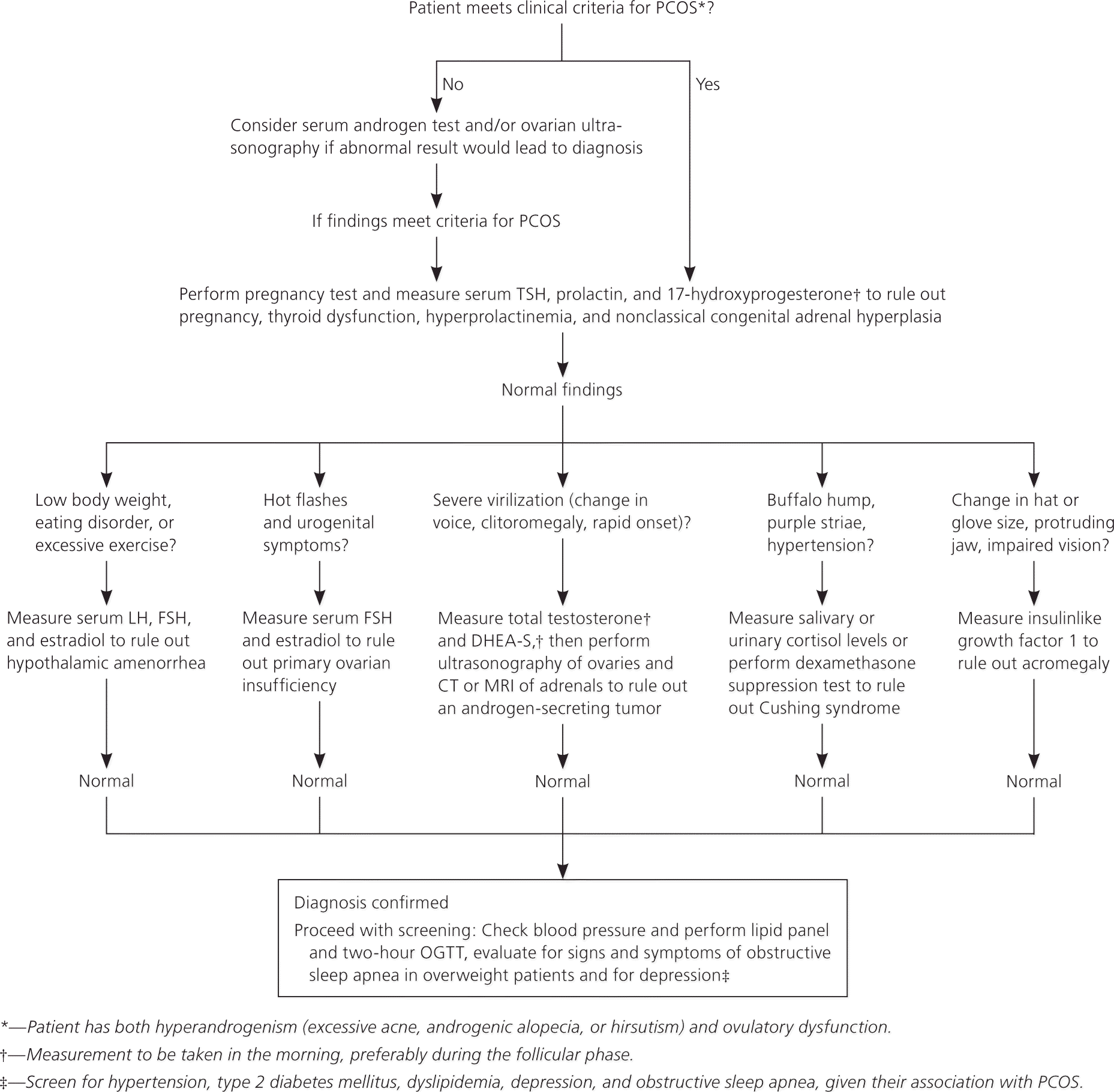
There is no one special test that can determine a pcos diagnosis. Unlike other medical conditions, the diagnosis of pcos is based largely on a process of elimination. Learn how to approach your diagnosis !
Take this simple quiz to get. Irregular periods, higher levels of androgen (male hormones) shown in blood tests or through symptoms like. First, you should review the following checklist to identify potential symptoms that you or she may be suffering from:
A diagnosis of pcos can usually be made if other rare causes of the same symptoms have been ruled out and you meet at least 2 of the following 3 criteria: High androgen levels are considered key to diagnosing pcos even though some women with the disorder do not have excess androgen. Do you suspect you have pcos?
A complete history and physical exam are critical for the diagnosis of pcos. Polycystic ovary syndrome, or pcos, is one of the most common ovulatory disorders 100 mi. Irregular periods or no periods.
Two out of three diagnostic criteria rely on history and physical exam, including menstrual history. Pcos is diagnosed when there is an overproduction of androgens (male hormones), absence of ovulation in the ovaries and presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries. Criteria for a diagnosis of pcos.
Instead, doctors must rely on symptoms, blood tests, a physical exam, and sometimes a pelvic ultrasound to determine. A history of irregular menstrual cycles, no ovulation (anovulation), facial hair, acne, hair thinning, recurrent. The endocrine society advises clinicians to diagnose pcos using the 2003 rotterdam criteria ( table 1 19 ), although recommendations differ across guidelines.
Once the patient has established care with.